View(Controller) & Template
장고에서 모델을 통해 데이터베이스에서 정보를 저장하고 읽어오는 것을 해보았다.
그전까지는 모델을 shell에서만 사용했다면 이제는 코드 상(views.py)에서 사용해보자
from django.urls import path
from . import views
app_name = 'polls'
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.index, name='index'),
path('<int:question_id>/', views.detail, name='detail'),
]
urls.py로 요청이 들어오면 views의 해당 메소드에서 처리하는 방식이다.
상세 페이지도 만들기 위해 url에서 숫자를 입력받을 수 있게 해준다. 그리고 views의 detail메소드로 연결되게끔
'<int:question_id>/' URL 패턴의 일부분으로 경로에 정수 값이 포함된 경우
해당 값을 question_id라는 이름으로 뷰 함수로 전달 할 수 있다.
그리고 app_name라는 namespace가 있다.
한 프로젝트에 여러 앱이 있다면 detail이 많을 수 있다.
예를 들어 Q&A에서도 질문에 따라 detail이 있고
커뮤니티도 글에 따라 detail이라는 이름을 사용하고 싶을 수 있다.
이때는 url 앞에 namespace을 지정해 줄 수 있다. (뒤에 ulr을 불러서 사용 할 때 사용)
# from django.http import HttpResponse
from .models import *
from django.shortcuts import render
def index(request):
latest_question_list = Question.objects.order_by('-pub_date')[:5]
context = {'questions': latest_question_list}
# return HttpResponse(latest_question_list)
return render(request, 'polls/index.html', context)
def detail(request, question_id):
question = Question.objects.get(pk=question_id)
return render(request, 'polls/detail.html', {'question': question})
현재 index메소드에서는 출력되는 question 목록을 출력하려고 한다.
HttpResponse로 질문목록을 반환하는 것이 아닌 HTML 활용해서 더 깔끔하게 data를 표시한다.
-> templates/polls 폴더 새로 만들고 안에 index.html파일을 만들자.

화면을 표시하기 위해서는 django의 render 함수를 사용한다.
이 때 model로 읽어온 값을 딕셔너리 형태로 template에 전달하려 한다.
Question에서 최근순 5개의 object 가져오고 latest_question_list 에 저장한뒤
딕셔너리 형태로 context에 저장한다.
이 context변수를 render 함수로
{% if questions %}
<ul>
{% for question in questions %}
<li><a href="{% url 'polls:detail' question.id %}">{{ question.question_text }}</a></li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
{% else %}
<p>no questions</p>
{% endif %}
<h1>{{ question.question_text }}</h1>
<ul>
{% for choice in question.choice_set.all %}
<li>{{ choice.choice_text }}</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
template에서는 전해진 변수(context의 question)를 사용하려면 중괄호로 변수를 묶어준다.
변수만 출력하면 model의 str이 출력된다.
지금 까지 뷰에서 템플릿을 연결하고 템플릿에 변수 전달해서 화면 표시
<li>{{first question}}</li>
추가
- template에서는 list를 indexing 할때 [0]가 아닌 .0으로 해준다.
- template 안에서 반복문을 쓰려면 {%%}안에 반복문 쓴다. 그리고 반복문 종료되기를 원하는 곳에 {%end for%}해준다.
- 즉 template안에서 변수를 쓰려면 {{}}를 쓰고 제어문 쓰고 싶으면 {%%}안에 제어문 적는다.
- 참고로 template안에서 choice의 모든 목록을 받아올떄는 question.choice_set.all 뒤에 ()안붙인다.
<a href="/polls/{{question.id}}"{{question.question_text}}</a>위의 url대신에 전체 적지 않고 코드를 통해 얻어오는 방법을 쓴다.
path에서 이름을 detail이라 주었기 때문에 url의 이름을 전달해주는 방식으로
<li><a href="{% url 'polls:detail' question.id %}">{{ question.question_text }}</a></li>
정리하자면 이렇게 template에서 url 태그를 통해서 링크를 걸 수 있다.
(url.py에서 app_name을 정하고 path에서 정한 이름을 이용해 url을 불러서 사용 polls:detail)
에러 처리하기
보통 웹페이지에서 사용자가 잘못된 요청을 주었을 때 서버는 에러를 준다.(ex. question/100)

우리가 만든 polls앱도 마찬가지


하지만 여기서는 404가 아닌 500에러가 나온다(서버 자신이 문제라는 뜻)
따라서 404에러가 발생하도록 바꿔줘야한다.

코드를 자세히 살펴보면 get으로 찾지 못해 에러를 발생하는 것을 확인할 수 있다.(get은 없으면 에러)
이때 장고 서버에서는 500코드를 내려주게 되는데 이것을 설명할 수 있는 404 에러로 바꿔주자.
에러의 처리는 try-except를 이용해서 처리해주면 된다.
from models.py import *
from django.http import Http404
from django.shortcuts import render
def detail(request, question_id):
try:
question = Question.objects.get(pk=question_id)
except Question.DoesNotExist:
raise Http404("Question does not exist")
raise HTTP404()로 404메세지를 사용자에게 보여준다.

하지만 try_except는 너무 길고 404는 자주 사용하므로 get_object_or 404 shortcuts를 제공해준다 ^_^
from django.shortcuts import render , get_object_or_404
def detail(request, question_id):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id)
return render(request, 'polls/detail.html', {'question': question})
투표 기능 만들기
<form action="{% url 'polls:vote' question.id %}" method="post">
{% csrf_token %}
<h1>{{ question.question_text }}</h1>
{% if error_message %}
<p><strong>{{ error_message }}</strong></p>
{% endif %}
{% for choice in question.choice_set.all %}
<input type="radio" name="choice" id="choice{{ forloop.counter }}" value="{{ choice.id }}">
<label for="choice{{ forloop.counter }}">
{{ choice.choice_text }}
</label>
<br>
{% endfor %}
<input type="submit" value="Vote">
</form>
for문 돌면서 <input> <label> <br> 을 하나씩 출력해준다.
{{forloop.counter}}는 for문이 돌때마다 1부터 1씩 증가한다.


하지만 여기서 vote를 누르면 CSRF 403 에러나온다.
{% csrf_token %} 넣어주면 자동으로 생성된다. 그리고 vote를 누르면 토큰 전달된다.
아직 vote는 안올라간다. 이제 form action의 주소를 설정해서 투표를 받는 기능을 만들어줘야한다.
먼저 path 경로 추가 해주고 vote 메서드 구현
urlpatterns = [
path('', views.index, name='index'),
path('<int:question_id>/', views.detail, name='detail'),
path('<int:question_id>/vote/', views.vote, name='vote'),
]
def vote(request, question_id):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id)
try:
selected_choice = question.choice_set.get(pk=request.POST['choice'])
except (KeyError, Choice.DoesNotExist):
return render(request, 'polls/detail.html', {'question': question, 'error_message': '선택이 없습니다.'})
else:
selected_choice.votes += 1
selected_choice.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('polls:index'))
여기서 pk=request.POST['choice'] 는 form에서 POST로 받아온 값 중에 'choice'를 가져오게 된다.
그리고 selected_choice의 votes를 1증가한뒤 table에 저장하는 방식이다.
투표가 완료되면 polls.index로 Redirect하게 설정

하지만 아무것도 선택 안하고 vote하는 경우 에러난다. 왜냐하면 choice를 읽어올 수 없기 때문

따라서 try-except를 사용해 에러메세지 표시되도록 해야한다.
{% if error_message %}
<p><strong>{{ error_message }}</strong></p>
{% endif %}
detail.html에서 if error_message -> error message가 있는 경우에만 표시되도록

추가로..
에러방어1
except (KeyError, Choice.DoesNotExist)에서
KeyError 는 아무것도 선택하지 않았을 경우
Choice.DoesNotExist는 여기서 없는 Choice를 선택했을 경우
짧은 순간이지만 그 사이에 삭제되어 없는 아이디가 올라올 수 있다.
예를 들어 vote를 누르기전 '바다'라는 선택지가 사라진다면?
그러면 does_notexit 에러 발생한다.
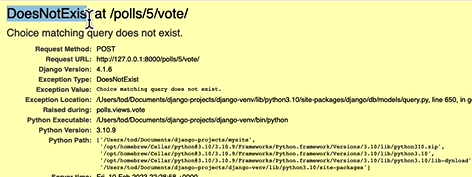
에러방어 2
만약 A와 B가 정말 동시에 녹차라는 것을 선택하고 Vote를 눌렀다면?
대부분의 사용서비스는 하나의 db를 두고 여러 서버를 운영한다.
A,B가 서로 다른 장고 서버에 접속했다고 생각해보자.
이 때 만약 question.choice_set.get()을 한다면 A서버에서 vote는 0 B서버에서도 vote는 0이다.
그리고 동시에 1을 증가시키면 둘다 vote=1이 되고 save하면 vote=1이 되게 한다.
따라서 1이 증가하는 연산을 서버가 아닌 db내에서 한다.
이런 경우는 서버는 두대더라도 db는 하나이기 때문에 방지 할 수 있다.
from django.db.models import F
def vote(request, question_id):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id)
try:
selected_choice = question.choice_set.get(pk=request.POST['choice'])
except (KeyError, Choice.DoesNotExist):
return render(request, 'polls/detail.html', {'question': question, 'error_message': f"선택이 없습니다. id={request.POST['choice']}"})
else:
# A서버에서도 Votes = 1
# B서버에서도 Votes = 1
selected_choice.votes = F('votes') + 1
selected_choice.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('polls:index'))
투표 결과 화면 만들기
result함수(View)
def result(request, question_id):
question = get_object_or_404(Question, pk=question_id)
return render(request, 'polls/result.html', {'question': question})
url 추가
path('<int:question_id>/result/', views.result, name='result'),
template 만들기
<h1>{{ question.question_text }}</h1><br>
{% for choice in question.choice_set.all %}
<label>
{{ choice.choice_text }} -- {{ choice.votes }}
</label>
<br>
{% endfor %}
이 때 투표 후 redirect 화면을 result 화면으로 하기 위해서
def vote(request, question_id):
...
else:
selected_choice.votes = F('votes') + 1
selected_choice.save()
return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('polls:result', args=(question.id,)))
여기서 result의 url은 question_id 가 필요하다. 이때는 args를 통해 question_id,를 전달(, 빼주면 안됨)
* args, ** kargs
'Python > Django' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Django 기본(3) (0) | 2024.10.15 |
|---|---|
| Django 기본(1) (0) | 2024.10.11 |
